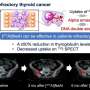
A novel treatment approach using astatine-211 (211At) has demonstrated potential for patients with thyroid cancer that is resistant to conventional therapies. In a groundbreaking study, researchers found that a single dose of this alpha-emitting radionuclide was not only well-tolerated but also effective in achieving disease control. This development offers hope for individuals whose conditions have not responded to standard radioactive iodine, which is the prevalent beta-emitting treatment for thyroid cancer.
Promising Results from First-in-Human Study
The findings from this first-in-human study were published in the December 2023 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The research team conducted trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of 211At in patients who had exhausted their treatment options. The results indicate that patients receiving this targeted alpha therapy experienced significant disease control without the need for molecularly targeted drugs.
Thyroid cancer, while often treatable with radioactive iodine, can develop resistance, making it challenging to manage for some patients. Traditional treatments are limited in their effectiveness once this resistance develops. The introduction of alpha therapy represents a shift in treatment paradigms, potentially offering a new avenue for those facing difficult prognoses.
Implications for Future Cancer Treatments
The success of this study suggests that targeted alpha therapy could play a crucial role in the treatment landscape for thyroid cancer and possibly other malignancies. By focusing on the unique properties of alpha particles, which can deliver a more concentrated dose of radiation directly to cancer cells, this approach minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
The research team emphasizes the importance of further studies to confirm these initial findings and understand the long-term outcomes associated with 211At treatment. If successful, this therapy could significantly improve survival rates and quality of life for patients battling resistant thyroid cancers.
As the medical community continues to explore innovative treatments, the promising results of this study underscore the potential for targeted therapies in advancing cancer care. This breakthrough reflects ongoing efforts to develop effective solutions for patients who currently face limited options due to treatment resistance.