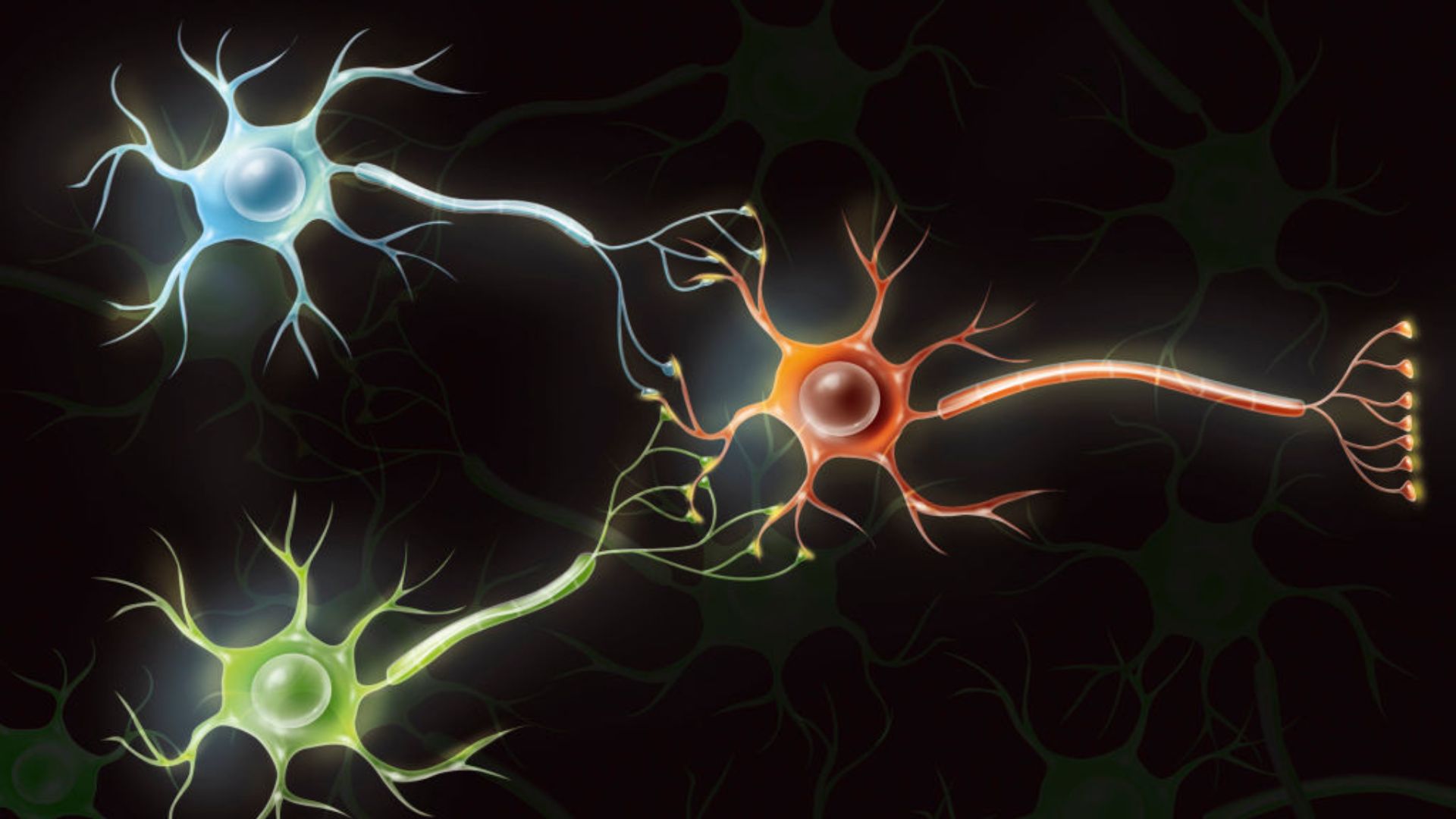
Advancements in biotechnology have led scientists at the University of California, San Diego to develop a groundbreaking concept: transforming human brain cells into functional biocomputers. This innovative approach utilizes biologically derived materials—such as DNA, proteins, and lab-grown neurons—to perform complex computational tasks.
The research team has successfully demonstrated that living neural cells can be programmed to execute calculations and respond to environmental inputs, marking a significant step towards the integration of biological systems with traditional computing. The potential applications for these biocomputers are vast, ranging from advanced data processing to novel solutions in artificial intelligence.
Understanding Biocomputing
A biocomputer operates by leveraging the inherent properties of biological materials. Unlike conventional computers that rely on silicon-based technology, biocomputers can utilize the natural capabilities of living cells to process information. This involves harnessing the electrical signals generated by neurons, which can communicate and perform computations similarly to electronic circuits.
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical exploration. The scientists believe that biocomputers may be instrumental in creating more efficient and sustainable computing technologies. By utilizing organic materials, these systems could reduce energy consumption significantly compared to traditional computers.
According to the team, the ability to manipulate brain cells for computational purposes could revolutionize fields such as medicine, environmental monitoring, and even robotics. For instance, biocomputers could be employed to develop smart sensors capable of detecting diseases or monitoring environmental changes in real-time.
The Future of Computing
As this research progresses, the potential for biocomputers to enhance computing capabilities is becoming increasingly clear. The team is currently working on refining their techniques to improve the efficiency and reliability of these biological systems. They aim to increase the complexity of tasks that biocomputers can perform, paving the way for more sophisticated applications.
The ethical considerations surrounding the use of human brain cells in technology are significant. Researchers are committed to addressing these concerns transparently, ensuring that their work aligns with ethical standards and respects the complexities of human biology.
The study is set to be published in a peer-reviewed journal in March 2024, providing further insights into the methodologies and findings of this innovative research. As scientists continue to explore the intersection of biology and computing, the emergence of biocomputers may lead to transformative changes in how we understand and utilize technology in the future.
This research represents not only a technical achievement but also a leap towards a new era of computing that could redefine our relationship with machines and biological systems.