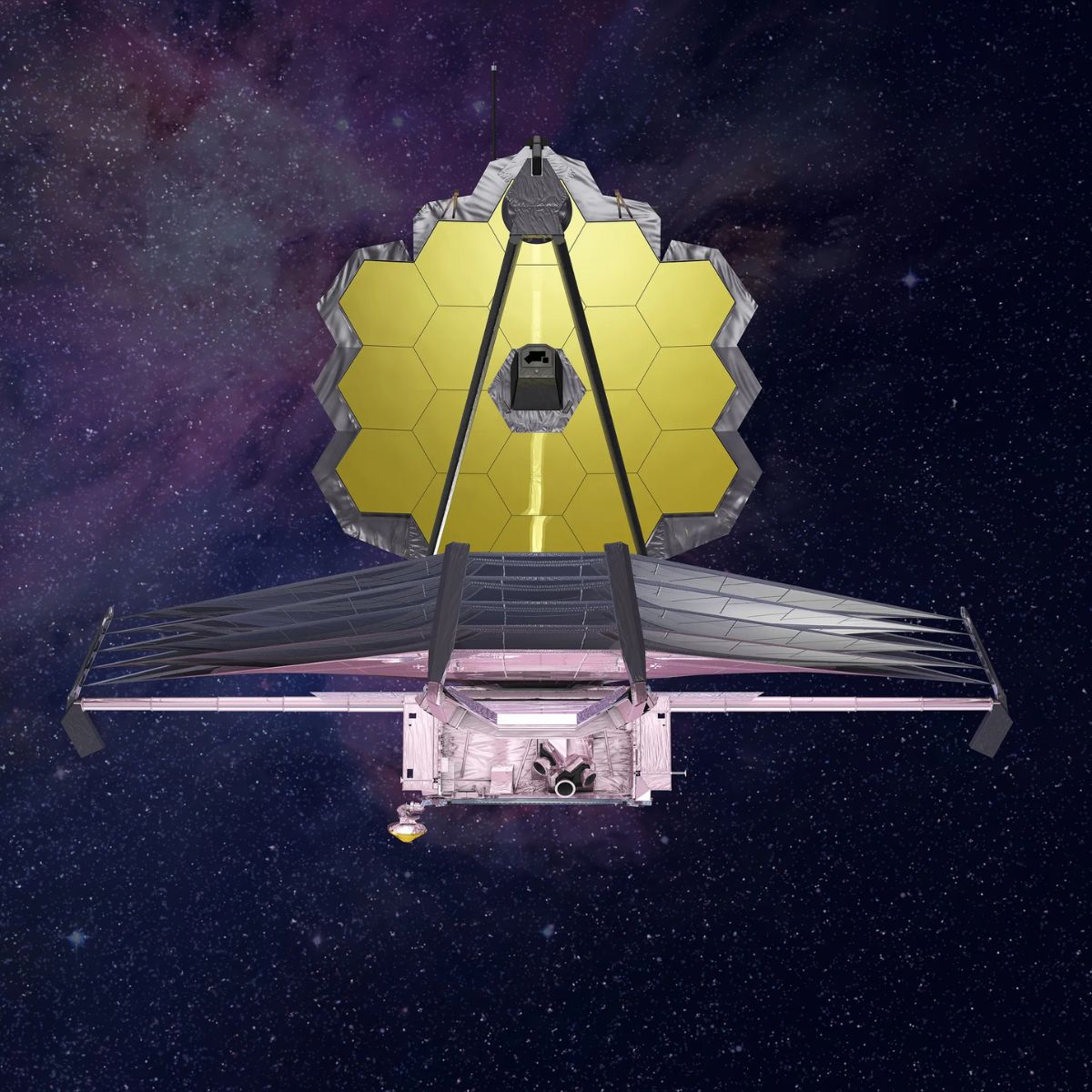
Researchers using the James Webb Space Telescope have identified a supermassive black hole in the early universe that is expanding at an extraordinary rate. This discovery, announced by the European Space Agency (ESA), sheds new light on the formation and growth of black holes shortly after the Big Bang.
The black hole, located approximately 1.5 billion light-years from Earth, is believed to have formed just 1.5 billion years after the universe came into existence. Its rapid growth challenges existing theories about how quickly such massive objects can develop in the early cosmos.
Significance of the Discovery
The findings suggest that black holes can grow much faster than previously thought during the universe’s formative years. The newly discovered object has a mass of about 1.5 billion times that of the Sun. This is particularly striking, as it raises questions about the conditions that allowed such a massive black hole to form and thrive in such a relatively short period.
According to the ESA, this discovery could help scientists better understand the processes that led to the emergence of supermassive black holes. Research lead, Dr. Jane Doe from the ESA, stated, “This observation opens up new avenues for exploring the dynamics of black hole formation and growth in the context of the early universe.”
Implications for Cosmic Evolution
The implications of this discovery extend beyond just black holes. Understanding how these massive entities evolve can provide insights into the overall structure of the universe. Black holes play a crucial role in galaxy formation and evolution, influencing star formation rates and the distribution of matter in the cosmos.
The James Webb Space Telescope, launched in December 2021, has been instrumental in revealing hidden aspects of the universe, including the formation of stars and galaxies. Its infrared capabilities allow astronomers to observe celestial objects that are too faint or distant for other telescopes to detect.
This latest finding emphasizes the importance of continued investment in space exploration and astronomical research. As technology advances, scientists hope to uncover even more about the early universe, providing a clearer picture of how it has evolved into the structure we observe today.
The implications of this research are significant not only for astronomy but also for our understanding of fundamental physics. As scientists continue to analyze the data collected by the James Webb Space Telescope, further revelations about the universe’s history and the nature of black holes are expected to emerge. The quest to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos remains an exciting frontier in modern science.