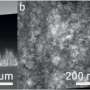
Recent research has unveiled that tiny particles of cosmic dust play a crucial role in hastening the formation of the complex organic molecules essential for life. Conducted by scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and published on September 21, 2023, this study sheds light on the potential for these particles to influence the development of life beyond Earth.
The team, which included researchers from NASA, employed laboratory simulations to replicate conditions found in space. They discovered that cosmic dust can act as a catalyst, significantly speeding up the chemical reactions required to form amino acids and other organic compounds. These molecules are fundamental building blocks for life, suggesting that the presence of cosmic dust could enhance the likelihood of life emerging in various environments across the universe.
Dr. Mark D. B. Johnson, a lead researcher on the study, emphasized the implications of these findings. “Understanding how cosmic dust contributes to the formation of life’s building blocks helps us explore the potential for life in environments previously thought to be inhospitable,” he stated. This research not only broadens our knowledge of astrobiology but also influences how scientists search for extraterrestrial life.
Implications for Astrobiology and Space Exploration
The findings could significantly impact future astrobiological studies. As researchers analyze the conditions on other celestial bodies, such as Mars or the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn, understanding the role of cosmic dust may provide insights into where to look for signs of life. The study suggests that environments rich in cosmic dust could be more favorable for life than previously anticipated.
With ongoing missions to explore the solar system, including NASA’s Artemis program aiming to return humans to the Moon, the timing of this research is particularly relevant. As space agencies prepare for missions to distant worlds, knowledge about the potential for life-supporting conditions becomes increasingly vital.
The study raises intriguing questions about the origins of life on Earth as well. Scientists have long pondered how organic molecules formed in the early solar system. If cosmic dust indeed accelerated this process, it could shift the paradigm of how we understand the emergence of life on our planet.
Future Research Directions
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to conduct additional experiments to explore the specific mechanisms by which cosmic dust facilitates the formation of organic molecules. They aim to identify the types of dust particles most effective in these processes and investigate their distribution across various celestial bodies.
This research not only enhances our understanding of life’s potential beyond Earth but also underscores the interconnectedness of cosmic events and biological processes. As scientists continue to probe the mysteries of the universe, the role of cosmic dust will remain a critical area of study in the quest to answer fundamental questions about life itself.
In summary, the study led by UCLA researchers marks a significant step forward in astrobiology, revealing that cosmic dust may play a vital role in the development of life’s building blocks in space. This discovery opens new avenues for exploration and enhances our understanding of the conditions that could foster life beyond our planet.