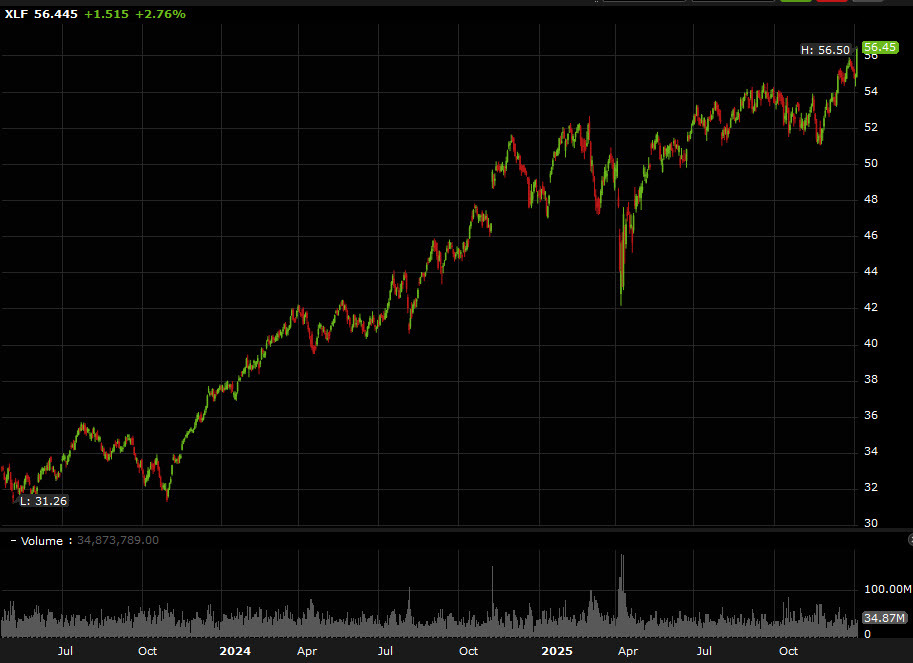
The financial sector demonstrated impressive growth in 2025, with several key players showing strong performance that has carried into the early months of 2026. The XLF financials exchange-traded fund (ETF) increased by 13.6% last year, buoyed primarily by significant gains from institutions such as Wells Fargo, which saw a 23.2% return, and JPMorgan Chase, with a 21.4% increase. Notably, Citigroup emerged as a smaller holding in the ETF, registering a remarkable rise of over 70%.
As the market shifts its focus from chip manufacturers to users of artificial intelligence (AI), financial institutions are positioning themselves as early adopters of this technology. The potential benefits of AI integration could serve as a substantial boost to profitability within the sector. In fact, the XLF has already experienced a 2.7% increase today, highlighting ongoing investor confidence.
Financial institutions possess two critical elements necessary for AI profitability: vast amounts of complex data and a workforce that often engages in repetitive, labor-intensive tasks. According to research from Citigroup, approximately 54% of roles in banking are at risk of being displaced by AI advancements. Should Citigroup decide to reduce its workforce by 20,000 to 25,000 employees—about 10% of its total 230,000 employees—it could achieve annual savings of approximately $2.5 billion, translating to a 12-14% increase in post-tax earnings per share.
Beyond workforce implications, AI could also enhance the financial sector’s lending and risk management capabilities. Improved accuracy in assessing borrower reliability could lead to more profitable lending practices. Similar advancements may also be seen in the fields of insurance and capital markets, further propelling the sector’s growth.
Despite these promising developments, there are concerns regarding the sustainability of profitability as broader economic conditions evolve. Analysts warn that markets may be overestimating the potential for profitability improvements while neglecting the risks associated with increased unemployment from AI and robotics. A rise in job losses could negatively impact bank lending and overall financial performance.
Currently, the market appears to be at a phase where the potential upsides of AI integration are heavily factored into stock prices. This trend is expected to persist throughout 2026, particularly for institutions that were undervalued at the beginning of the year. As financial firms navigate the balance between embracing technological advancements and managing the associated risks, their performance will be closely monitored by investors and analysts alike.