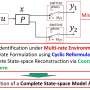
A team of researchers at Kumamoto University in Japan has developed a groundbreaking mathematical framework that enables accurate modeling of complex systems utilizing multiple sensors operating at varying sensing rates. This significant advancement stands to enhance the functionality and reliability of technologies in diverse fields such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and sensor networks.
The innovative framework allows for the integration of data from different sensors, each functioning at its own pace. This capability is crucial in environments where real-time decision-making is essential. For instance, autonomous vehicles require precise data from various sensors to navigate safely and efficiently on busy roads. Enhancing these systems could lead to increased safety and reduced accidents involving self-driving cars.
Implications for Technology and Safety
As technology continues to evolve, the need for reliable sensor systems becomes increasingly important. The research team at Kumamoto University has identified that traditional modeling techniques often struggle to account for the discrepancies in sensing rates. By addressing this challenge, their new mathematical framework could redefine how sensor systems are constructed and managed.
Smart robots, which are increasingly being deployed in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, also stand to benefit significantly from this advancement. Improved sensor modeling could enhance their ability to interact with dynamic environments and carry out complex tasks more effectively.
Moreover, sensor networks, which play a critical role in areas such as environmental monitoring and smart city infrastructure, could see improved performance and reliability. The ability to accurately model these networks can lead to better data collection and analysis, ultimately supporting more informed decision-making.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to further refine their mathematical model and explore its applications in various sectors. They aim to collaborate with industry partners to implement their framework in real-world systems, particularly in areas where safety and efficiency are paramount.
Given the rapid advancements in technology and the growing reliance on sensors, this research could not only contribute to the development of safer autonomous systems but also inspire future innovations in sensor technology. As the study continues, the potential for widespread adoption of these methodologies could reshape the landscape of numerous industries.
In summary, the work done by the team at Kumamoto University represents a vital step forward in the modeling of complex sensor systems. With applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to smarter robots, this new mathematical framework is poised to transform how we approach sensor technology in the years to come.