This week, remarkable scientific discoveries have emerged from various corners of the globe, revealing insights into ancient human populations, cosmic phenomena, and modern technological advancements. Notably, researchers have identified a human population in southern Africa that remained genetically isolated for approximately 100,000 years, while astronomers have located the largest spinning object in the universe, located over 140 million light-years away.
Ancient Humans and Cosmic Discoveries
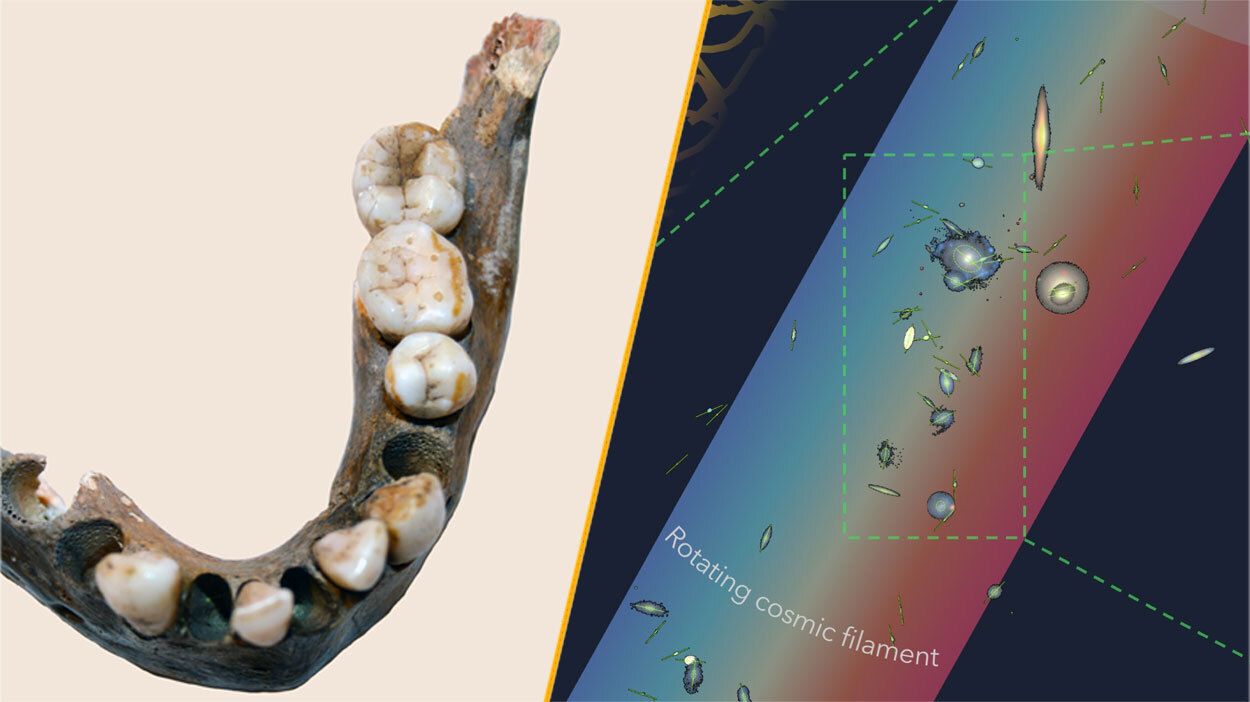
In southern Africa, a recent study examined skeletons dating back up to 10,000 years, discovered south of the Limpopo River, which flows from South Africa into Mozambique. The researchers found that individuals who lived more than 1,400 years ago exhibited a vastly different genetic makeup compared to modern humans. According to the study, these ancient people “form an extreme end of human genetic variation,” highlighting the diversity of human genetics throughout history.
Meanwhile, astronomers have turned their attention to a cosmic marvel. They have discovered the largest spinning structure in the known universe, a massive rotating filament that is wider than the Milky Way. This colossal filament, linked to a daisy-chain of 14 galaxies, is spinning at an astonishing 68 miles per second (or 110 kilometers per second). This discovery deepens our understanding of the universe’s structure and dynamics.
Archaeological Finds and Environmental Challenges
In China, archaeologists have unearthed a significant pit filled with skulls near a 4,000-year-old city. This remarkable find has raised questions due to the predominance of male skulls, a deviation from typical sacrificial practices observed in nearby settlements. The unusual nature of this discovery invites further investigation into the societal norms of ancient cultures.
Additionally, a 2,700-year-old elaborate tomb in Greece has piqued the interest of researchers, as it contains a woman adorned with an upside-down crown, prompting speculation about its significance in historical context.
In modern environmental news, a decades-long initiative in China, known as the Great Green Wall, aimed at combating desertification, has revealed unintended consequences. While the tree-planting project has succeeded in staving off desertification, it has altered rainfall and evaporation patterns across the country. A recent analysis indicates that these changes have led to reduced water levels in some of the most populous regions, highlighting the complexity of large-scale ecological projects.
Researchers are also revisiting the validity of the world’s hottest temperature record, set in Death Valley in 1913. New findings suggest that human error may have contributed to this extreme reading, prompting discussions about the reliability of historical weather data. In Europe, a concerning study warns that the collapse of a key Atlantic current could lead to extended periods of drought, affecting millions.
In a fascinating development, interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS has captured the attention of scientists. Recent observations from the Joan Oró Telescope in northeastern Spain have revealed that the comet is exhibiting signs of “ice volcanoes,” with spiral jets shooting from its surface. As the comet approaches the sun, it heats up rapidly, indicating that ice is sublimating from its surface—paralleling phenomena observed in other solar system objects.
Innovations in Water Extraction and Helium Reserves
On the technological front, engineers at MIT have unveiled an innovative method to extract drinking water from air, even in arid regions. This new technique employs ultrasound to efficiently shake water droplets from spongy materials, achieving a remarkable 45 times more efficiency than traditional evaporation methods. While the device requires a power source, researchers are optimistic about pairing it with solar cells to make it more sustainable.
Moreover, the discovery of carbon-free helium reservoirs hidden in ancient rocks could revolutionize the helium industry, addressing the looming shortage of this vital resource used in medical and technological applications. As scientists explore these new findings, the potential for sustainable helium extraction represents a significant advancement.
As this week has shown, the realms of ancient history, cosmic exploration, and innovative technology continue to unfold, revealing the complexity and interconnectedness of our world and beyond.